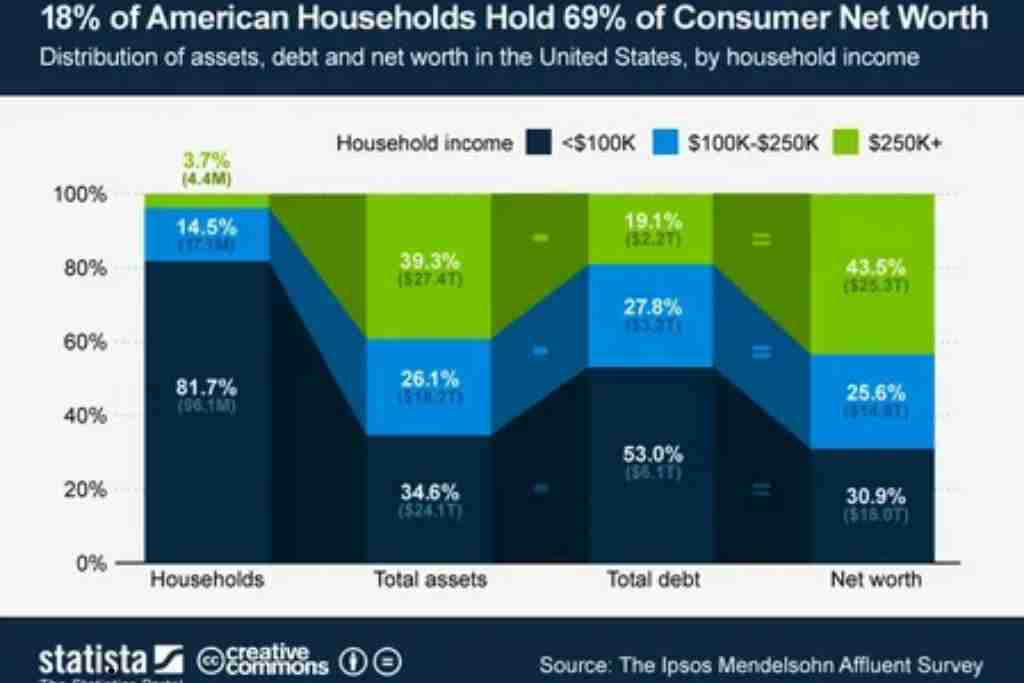
Average Net Worth is a crucial indicator of financial health, reflecting an individual’s or household’s assets minus their liabilities. In the United States, net worth varies significantly based on factors such as age, education, income, and geographical location. This article provides an in-depth analysis of the average net worth in the USA, how it compares across different demographics, and ways to improve financial standing.
Understanding Net Worth
Net worth is calculated by subtracting total liabilities (debts) from total assets. Assets include real estate, investments, savings, and other valuable possessions, while liabilities encompass mortgages, student loans, credit card debt, and other financial obligations.
Why Net Worth Matters
Net worth serves as a financial snapshot, helping individuals gauge their financial progress over time. A positive net worth indicates financial stability, while a negative net worth suggests debt outweighs assets, requiring corrective financial planning.
- Explore more info about: Montana Jordan Net Worth 2025: The Superstar Emerges
Average Net Worth by Age
Net worth tends to increase with age as individuals accumulate savings, investments, and real estate assets. According to the Federal Reserve’s Survey of Consumer Finances (SCF), here’s how net worth varies by age group:
Under 35 Years
- Average net worth: $76,300
- Median net worth: $13,900
- Many young adults have significant student loan debt, impacting their net worth.
35-44 Years
- Average net worth: $436,200
- Median net worth: $91,300
- Individuals begin accumulating home equity and retirement savings.
45-54 Years
- Average net worth: $833,200
- Median net worth: $168,600
- Mid-career individuals experience income growth and investment appreciation.
55-64 Years
- Average net worth: $1,175,900
- Median net worth: $212,500
- Nearing retirement, individuals focus on maximizing retirement accounts.
65-74 Years
- Average net worth: $1,217,700
- Median net worth: $266,400
- Retirement savings and home equity contribute to financial security.
75+ Years
- Average net worth: $977,600
- Median net worth: $254,800
- Spending down retirement savings affects overall net worth.
Net Worth by Income Level
Net worth correlates strongly with income. Households in the top 10% of earners have substantially higher net worth than those in lower income brackets. According to the SCF:
- Bottom 20%: Average net worth of $6,030
- Middle 20%: Average net worth of $201,800
- Top 10%: Average net worth exceeding $5,000,000
Net Worth by Race and Ethnicity
Disparities in wealth exist among racial and ethnic groups due to historical and systemic economic inequalities.
- White households: Median net worth of $188,200
- Black households: Median net worth of $24,100
- Hispanic households: Median net worth of $36,100
- Asian households: Median net worth of $194,000
These gaps result from differences in homeownership rates, income levels, and access to generational wealth.
Net Worth by Education Level
Higher education levels generally lead to higher earnings and net worth.
- No high school diploma: Median net worth of $20,500
- High school graduate: Median net worth of $74,000
- Bachelor’s degree: Median net worth of $308,200
- Advanced degree: Median net worth of $625,500
Investing in education often yields long-term financial benefits, despite the initial burden of student debt.
Factors Affecting Net Worth
Several factors influence an individual’s net worth:
- Income Level: Higher earnings provide more opportunities for saving and investing.
- Debt Levels: High debt, particularly student loans and credit card debt, reduces net worth.
- Homeownership: Owning property builds equity over time.
- Investment Strategy: Diversified investments enhance wealth accumulation.
- Savings Rate: Consistent savings contribute to financial security.
- Economic Conditions: Inflation, interest rates, and stock market performance impact asset values.
How to Increase Your Net Worth
Improving net worth requires strategic financial planning. Here are some steps to enhance financial stability:
1. Reduce Debt
- Prioritize paying off high-interest debts like credit cards.
- Consider refinancing loans to lower interest rates.
- Make consistent mortgage payments to build home equity.
2. Increase Savings
- Establish an emergency fund with 3-6 months’ worth of expenses.
- Maximize contributions to retirement accounts like 401(k) and IRAs.
- Utilize employer-matching programs to boost savings.
3. Invest Wisely
- Diversify investments across stocks, bonds, and real estate.
- Take advantage of tax-advantaged accounts like Roth IRAs.
- Maintain a long-term investment strategy to capitalize on market growth.
4. Boost Income
- Seek career advancements or salary negotiations.
- Develop additional income streams such as freelancing or passive investments.
- Invest in skills and education to enhance earning potential.
5. Plan for Retirement
- Start saving early to leverage compound interest.
- Calculate retirement needs and adjust savings accordingly.
- Consider working with a financial advisor for personalized planning.
Conclusion
The average net worth in the USA varies significantly based on age, income, education, and demographic factors. While disparities exist, individuals can take proactive steps to increase their net worth through smart financial management. By reducing debt, increasing savings, and making informed investment choices, Americans can build long-term financial stability and security.
- Marla Maples Daughter: Unveiling the Life, Achievements, and Future of Tiffany Trump - March 21, 2025
- MrBeast Net Worth 2024: An In-Depth Look at the YouTube Sensation’s Wealth - March 20, 2025
- Angelina Jolie: A Closer Look at Her Life, Kids, and Legacy - February 24, 2025